Reflecting on 2022 and Looking Ahead Into 2023

The technology industry has been one of the most dynamic and fastest-growing sectors of the global economy in recent years. 2022 was a tale of two halves. The first half of the year (and even into Q3) continued on a positive note and benefited greatly from the COVID-induced growth on the user and innovation front. Globally, startups benefitted from the preceding year of funding strength which saw investors plough $621 billion into startups globally, including $20+ billion record funding for Southeast Asia startups.
Towards the second quarter of 2022, we surveyed our portfolio founders on the fundraising environment and business outlook. A clear majority of them were optimistic about the future, observed business growth but were already noticing the slowdown in fundraising. Amidst these uncertainties, three of our portfolio companies Deliveree, Believe, and Trusting Social raised approximately $180 million of funding (April to June 2022).
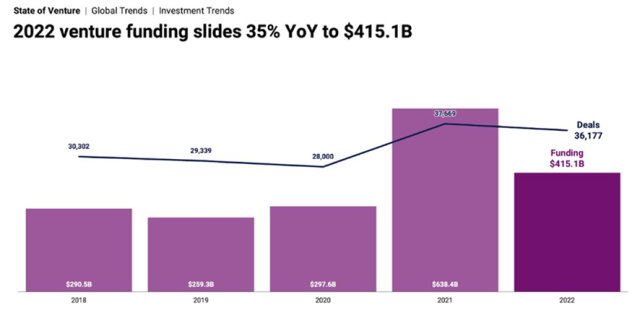
As we rolled Into the second half of 2022, and certainly more towards Q4, a new reality set in for the tech industry clouded by an array of challenges ranging from economic uncertainty, market volatility, geopolitical tensions and reverberating ripples from the pandemic. Venture investors slowed their pace of investing, due diligence took longer, valuations retreated, and we started seeing signed term sheets being delayed or even revoked. Round sizes also began shrinking and later stage startups struggled to raise growth capital while holding on to lofty valuations set during their prior fundraising rounds. Funding for tech companies globally declined to $415 billion, -35% YoY but remained healthy compared to pre-pandemic levels.
According to Carta and as a benchmark on valuation, 22% of US venture-backed companies in the US, both private and public, reduced their valuations in Q3 2022, nearly tripling year-over-year. Meanwhile, as the maxim goes, “flat is the new up” with 34% of companies witnessing a rise in their valuations — the lowest increase in five years.
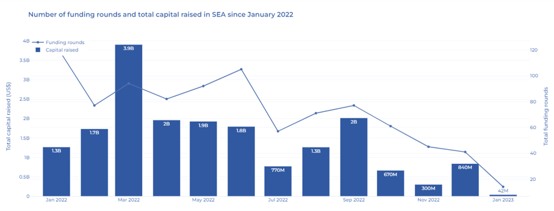
While the weakening fund raising environment became more evident as the year progressed, robust fundraising in the first half of the year more than compensated for the slowdown in the second half of the year with 887 funding rounds totaling US$28.8 billion in 2022 (compared to $25.7 billion raised in 2021), according to a TechinAsia report.
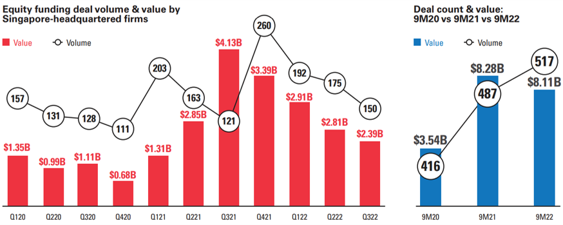
Referring to a joint DealstreetAsia and Enterprise Singapore report, Singapore-headquartered startups closed 517 deals in the first nine months of 2022 raising $8.11 billion, a little shy of the 487 deals and $8.28 billion raised in the same period of 2021, and with less dealmaking as the year prior.
VCs Prefer Early Stage, Late Stage Deals See Declining Investment Interest
Investment statistics from the earlier report also indicate VC preference towards early stage deals, which are defined as seed through Series B rounds. Late stage are attributed to Series C and above rounds. From the graph below extracted from the DealstreetAsia and EnterpriseSG report, investors have shifted their investment dollars into a larger number of smaller, earlier venture deals. The median size of seed rounds have doubled from $1.2-1.5 million in 2021 to $2.5-3.0 million in 2022. For later stage deals, the report also highlighted a contraction of deal value for Series D and E companies by 30-50%.
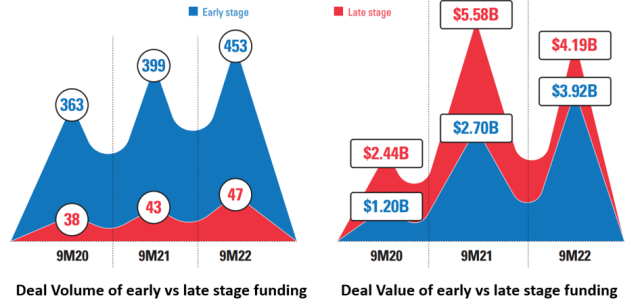
In the United States, startups seeking late-stage funding are failing to attract investors as dour sentiment in the public markets and dull exit conditions make it tougher to justify higher valuations. As valuations slip to reasonable levels and startups begin to trim operating expenses to get closer to cash or EBIDTA positive levels, they may once again start to look attractive to venture and PE investors who are keen to deploy their fund capital to work.
M&As & IPOs
We observed a notable rise in private-to-private mergers and acquisitions, as publicly-listed big tech companies saw a steep decline in their share price and valuation which in turn affected the SPAC and IPO listing opportunities. Completed venture-backed acquisitions in the first three quarters of 2022 totalled $81.7 billion, according to PitchBook data, down 40.7%, from $137.8 billion in the same period the year before. No significant venture-backed tech startups went public. In total, IPO deal proceeds plummeted 94% in 2022 — from $155.8 billion to $8.6 billion — according to Ernst & Young IPO report. Looking at 2023, there is an air of optimism that the IPO drought will “un-thaw” and favorable market conditions will return to allow the growing pipeline of IPO filings waiting to list – including Instacart (US), Vinfast (Vietnam), Tiktok (China), Stripe (US) and Epic Games (US).
On the M&A front, Microsoft reportedly acquired Fungible, a Santa Clara maker of data centre chips and storage device for $190m, about $134 million less than Fungible had raised in funding since its launch. Closer to home, according to a Tech in Asia report, Singapore-headquartered Amplify Health – a joint venture between AIA Group and Discovery Group – has announced its acquisition of AI-powered data analytics firm Aida Technologies. GoTo Group, the Indonesia-based tech giant, has acquired Swift Logistics Solutions for 583 billion rupiah (US$38 million).
Cryptopocalypse
A year in review would be incomplete without mention of the events that took place in the crypto space which was rocked by high-profile scandals through the year. Terra Luna for example, a cryptocurrency that was launched in 2019 as a stablecoin pegged to the U.S. dollar, witnessed a crash of its Terra (LUNA) crypto token in May 2022 from $120 to $0.02, a 99.9% correction. Forbes Digital Asset estimated that nearly $60 billion was wiped out of the digital currency space.
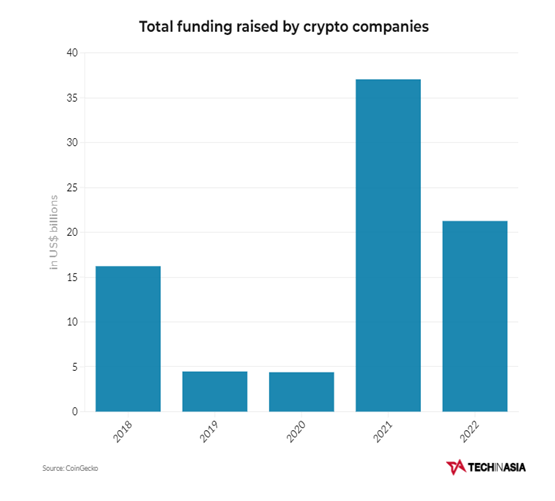
Three Arrows Capital (3AC), a crypto hedge fund founded in Singapore and believed to be managing around $10 billion in crypto assets, incurred significant losses due to its staked Luna position. 3AC has since filed for Chapter 15 bankruptcy proceedings in the US Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York to protect its US assets from creditors. And this triggered a contagion of Chapter 11 bankruptcy involving Voyager, BlockFi, Genesis Global and Celsius who had dealings with 3AC. And just before the year ended, the crypto industry experienced a Black Swan event that saw crypto exchange FTX valued at $32 billion based on its most recent funding round declared bankrupt. FTX Exchange was the world’s third largest cryptocurrency exchange specializing in derivatives and leveraged products. News around FTX’s leverage and solvency involving FTX-affiliated trading firm Alameda Research triggered a liquidity crisis when FTX’s customers demanded withdrawals worth $6 billion. FTX Token (FTT) is a utility token that provides access to the FTX trading platform’s features and services. The value of FTT fell by more than 80% within two days. The crypto industry is still reeling from a brutal 2022, having lost over US$2 trillion of its value throughout the year. Crypto companies still managed to raise a total of US$21.3 billion in funding in 2022, down 42.5% from the previous year.
Recalibration in 2023
The general consensus is that 2023 will remain challenged but with green shoots on the horizon. Negative macro conditions are set to continue into 2023 – sustained inflation, raised interest rates, Russia v Ukraine, China-Covid slowdown etc. However, there has also been positive news flow on many of these fronts in the past weeks (e.g. inflation levelling off; China emerging quicker than expected from Covid-slowdown, China tech reawakening etc).
Taken together, and as it relates to the tech industry, it seems 2023 will provide the backdrop for a healthy recalibration period for startups globally. In Southeast Asia, for example, where most founders have not yet experienced a significant market downturn, this has been (and will continue to be) an opportunity for founders to adjust internal KPIs towards a more sustainable growth and fundraising future. Creativity loves constraint and we believe that great startups, with solid fundamentals, will emerge winners in a tight operating and funding environment.
Cash is king. VCs are encouraging their portfolio companies to conserve cash and extend their cash runway into 2024 so as to be able to operate through some of these macro headwinds. To that end, it’s worth noting that the companies in Genesis Fund I Portfolio have a weighted average cash runway of approximately 17 months this quarter (up from 13.5 months in Q3 2022).
Profit before growth. Founders are expected to be more disciplined around spending and investors are edging these startups to turn “profitable”, the definition of which is wide, but in these times has come to prioritise a meaningful and sustainable business model.
Talent stocking. Hiring exceptional talent used to come at a premium but with many startups downsizing, startup founders can now hire more prudently with less pressure on the P&L. In Southeast Asia, it’s been reported that retrenched executives from tech companies (and new job seekers) are actively in the market looking for opportunities but with more modest salary expectations.
Dry powder. Venture firms have continued to raise record capital, even as startups received far less money than they did in 2022. Dry powder was estimated to be as high as $1.3 trillion globally for private equity and $580 billion globally for VC. While we do not expect VCs to invest at a pace comparable to 2021, there is pressure stemming from fund size, duration to deploy and the need to put capital to use. As previous downturns have clearly shown, investors with dry powder will find it a rewarding time to deploy capital, amidst more reasonable valuations and the ability to set better deal terms.
2023 Hot VC Target Sectors
January is a hotbed for new tech innovation unveiled to consumers through the annual Consumer Electronics Show held in Las Vegas USA. The 2023 show is focused on a number of areas, including the metaverse and Web3, digital health, sustainability, automotive and mobility, and human security for all. There was strong participation from Asia which include those from South Korea, which number more than 500 and include the likes of Samsung, SK, Hyundai Motor and LG, while just under 150 exhibitors hail from Taiwan. We highlight some interesting technology showcased at CES:
- Sony teamed up with Honda to exhibit a new brand of electric vehicle called the Afeela. The Afeela logo appears on a narrow screen, or “media bar,” on the vehicle’s front bumper. This can also interact with people outside the vehicle and share information such as the weather or the car’s state of charge. Unlike the car Sony showed off at CES 2020, this car is expected to hit the North American roads in 2026. Japan and Europe will follow.


- The battery-operated WasteShark by the Dutch firm RanMarine Technology is an autonomous surface vessel designed to remove algae, biomass, and floating pollution such as plastics from lakes, ponds, and other coastal waterways. At least 14 million tons of plastic end up in the ocean every year, and plastic makes up 80% of all marine debris found from surface waters to deep-sea sediments. Marine species ingest or are entangled by plastic debris, which causes severe injuries and death.


- Canadian-based eSight Eyewear plans to display a headset designed to help people with visual impairments such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD). AMD is an eye disease that can blur your central vision. It happens when aging causes damage to the macula — the part of the eye that controls sharp, straight-ahead vision. The macula is part of the retina (the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye). AMD happens very slowly in some people and faster in others. If you have early AMD, you may not notice vision loss for a long time; hence the importance of regular eye exams. Once the user puts on the device, they will be able to see distinct features such eyebrows, mouth and eyes.

- Singapore-based Igloo Company will show off its second generation of smart padlocks at CES, including a slimmed-down fingerprint-based model and another featuring enterprise-grade security. The latest smart padlocks will ship in the spring. The keypad-based Padlock 2 builds on the company’s original Bluetooth-enabled smart lock by manufacturing it to military standards, including a hardened steel case. The Padlock 2 gets eight months out of a single charge of its lithium battery (the original relied on disposable batteries), and its shackle can withstand up to 15kN of cutting force, 5kN of pulling force, and 100Nm twisting force.

- And last but not least, there has been immense interest in generative AI since ChatGPT came online and mesmerised consumers with its ability to provide real-time chat responses (see below). In 2019, Microsoft invested $1 billion in OpenAI, the tiny San Francisco company that designed ChatGPT. Microsoft is now poised to challenge Big Tech competitors like Google, Amazon and Apple with a technological advantage as it is rumoured to be in talks to invest another $10 billion in OpenAI. See the picture below (right column) where we tested Open AI’s ability to write a short paragraph on electric vehicles. Try it at https://chat.openai.com/chat


- Sony teamed up with Honda to exhibit a new brand of electric vehicle called the Afeela. The Afeela logo appears on a narrow screen, or “media bar,” on the vehicle’s front bumper. This can also interact with people outside the vehicle and share information such as the weather or the car’s state of charge. Unlike the car Sony showed off at CES 2020, this car is expected to hit the North American roads in 2026. Japan and Europe will follow.